Yet again, two flaws in Apache HTTP Servers expose 24 million Apache Servers to the Internet, with about 32% of them detected in the United States alone.
The Apache Software Foundation has published a new version 2.4.52 of the Apache HTTP Server to fix two vulnerabilities in one of the world’s most popular web servers – one of which is rated as high, and the other as critical.
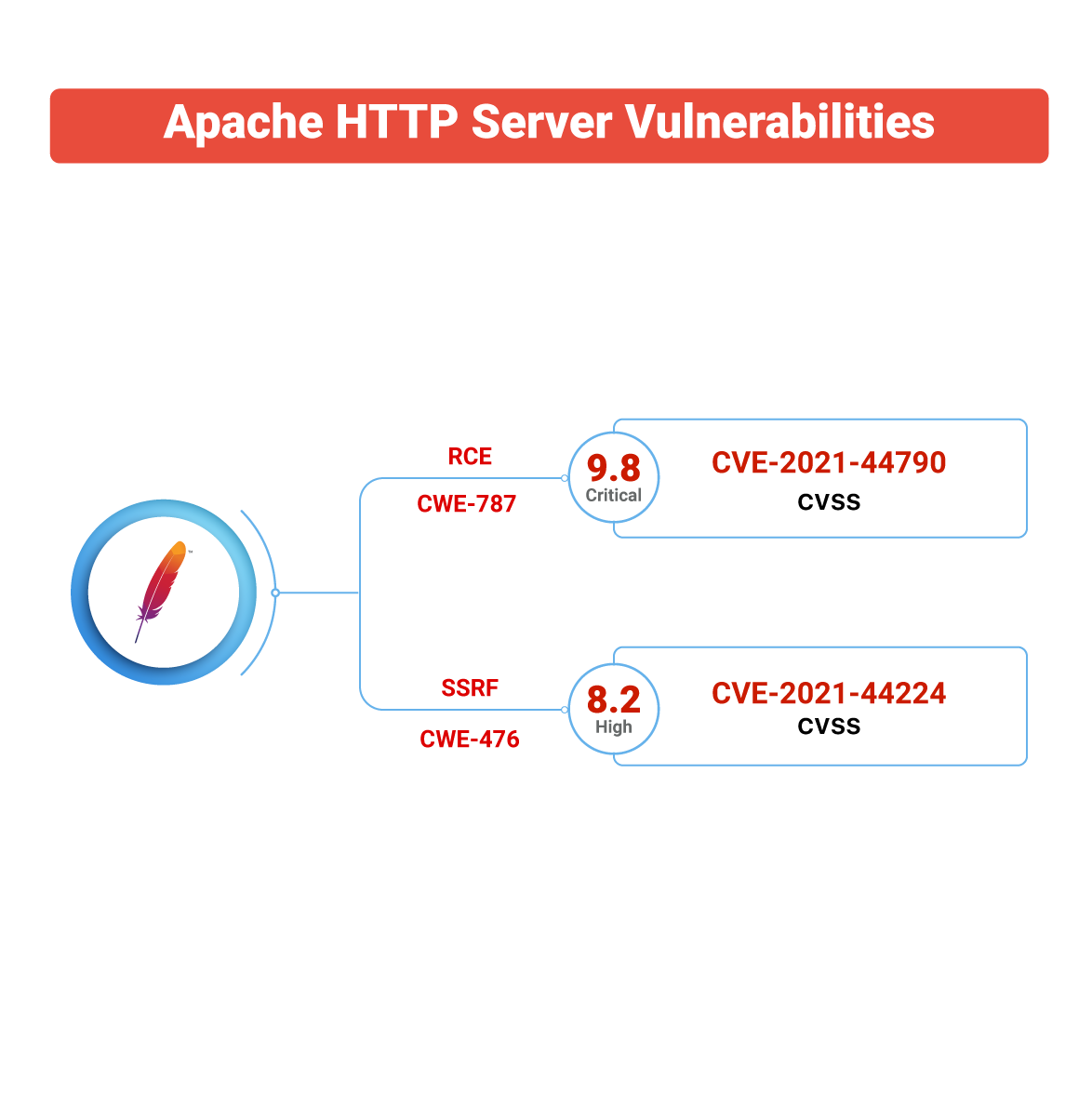
The CVE identifiers for two vulnerabilities are CVE-2021-44790 and CVE-2021-44224, one of which may allow a remote attacker to gain control of an affected system.
The Apache HTTP Server is a cross-platform web server that is free and open-source software distributed under the Apache Licence 2.0 and maintained by an open community of developers. Because of its multi-platform capabilities, security, and compatibility with the majority of computer operating systems, it is the world’s second most widely used web server-side application.
CISA, the US government’s security response agency, urges open-source community users to upgrade their outdated, vulnerable versions to the most recent ones right away.
The Findings
CVE-2021-44790
-
A well-crafted request body can trigger a buffer overflow in the mod_lua multipart parser (r:parsebody() called from Lua scripts).
-
A CVSS v3 score of 9.8 (critical) has been provided to this vulnerability.
-
This CVE falls under the vulnerability category described as CWE-787 (Out-of-bounds Write) which can result in corruption of data, a crash, or code execution. This CWE tops the 2021 Common Weakness Enumeration.
-
All the Apache HTTP Server prior to version 2.4.51 are affected.
-
Although the serious flaw has not yet been exploited, the HTTPD team believes it has the potential to be weaponized.
CWE-787 occurs because the memory buffer limits were not adequately checked throughout the operation execution. For instance, when creating string parsing routines, the function must keep track of the available and consumed buffers. When these two variables and their dependent variables are mishandled during function execution, the function might write beyond the available buffer and overwrite adjacent memory areas. An attacker can exploit this CWE to trigger a buffer overflow, which can be leveraged for a variety of attacks, including privilege escalation, remote code execution, and data leakage.
– Pentester’s Perspective
-
Google search interest for CVE-2021-44790 shows a high number of searches in China with fewer counts for Singapore, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and South Korea.
CVE-2021-44224
-
A crafted URI delivered to HTTPD configured as a forward proxy (ProxyRequests enabled) might cause a crash (NULL pointer dereference) or allow requests to be forwarded to a defined Unix Domain Socket endpoint in setups mixing forward and reverse proxy declarations (Server Side Request Forgery).
-
This vulnerability affects Apache HTTP Server 2.4.7 up to 2.4.51.
-
A CVSS v3 score of 8.2 (high) has been provided to this issue.
-
This CVE is classified under CWE-476, leading to NULL Pointer Dereference weaknesses in code that falls fifteen in the 2021 CWE Top 25 Most Dangerous Software Weaknesses.
-
Google search interest for CVE-2021-44224 shows a high number of searches in China with fewer counts for Taiwan, Hong Kong, South Korea, and Singapore.
Scanner Exposure
We examined the scanner exposure and found that the popular scanner Nexpose failed to detect these vulnerabilities.
The following are the plugin IDs that were able to detect these issues.
|
CVE ID |
Qualys |
Nexpose |
Nessus |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CVE-2021-44224 |
282186, 730313, 690751 |
NA |
156255, 156200, 156199, 113079 |
|
CVE-2021-44790 |
282186, 730312, 690751 |
NA |
156255, 156200, 156199, 113079 |
Yet to Be Weaponized
The Apache Foundation teams state in their study that they have no idea how the most significant weakness will be exploited. Hackers might, however, develop one and use it in attacks against web servers that have not yet been upgraded.
However, as Log4j demonstrated, potentially exploitable flaws can be problematic even on non-public servers if they are triggered by untrusted user data carried along by other internet-facing servers at your network edge.
Patching these two issues in Apache’s web server should be a top priority for site owners since the prominence of the Apache HTTP Server makes unprotected systems a prime target for hackers globally.
Global Exposure
The Shodan search engine indicates that 24 million product instances remain vulnerable to attacks if they are not patched immediately. 32% of the vulnerable systems are found in the United States, followed by Germany with 9 %. The following are the ports that are at risk.
What to do?
This isn’t the first time that a significant issue in the HTTP server has been fixed. When we consider that Apache is the second most used HTTP server behind Nginx, this is not an update that needs to be taken lightly. This platform would power around 25% of all websites on the globe. Beyond these two CVEs, there are other bug patches, so you should patch them to 2.4.52 as soon as possible.
Organizations and individuals who use Apache HTTP Server should review this notification and upgrade the software to the most recent version as soon as possible to protect themselves from potential attacks using this major weakness.
CSW’s Vulnerability Management as a Service (VMaaS) offers full coverage encompassing your entire IT landscape and detects, prioritizes,
and fixes vulnerabilities on your organizational infrastructure.
To know more about CSW’s Vulnerability Management as a Service (VMaaS),
please click here.









